Depending on what type of user you are, you will benefit more from one or the other type of disk drive. So, if you feel like your computer is getting slow, you might need to upgrade to a solid-state drive (SSD) which can influence better drive performance.
When it comes to a computer’s storage capabilities, there are two main types of drives: solid-state drives (SSD) and hard disk drives (HDD). Both have their own advantages and disadvantages, but which one is faster?
So hold onto your seats, because it’s time to see which one comes out on top in the ultimate showdown: SSD vs HDD.
This speed test guide compares SSDs and hard disk drives (HDDs) to determine which one is faster. To run this sort of test at home, start your free trial of Hard Disk Sentinel. In this blog post, we’ll break down the differences between these two storage options to help you make an informed decision on what type of drive is right for you.
SSD vs HDD – Which is Better?

To answer this question, we’ll need to take a closer look at the difference between SSDs and HDDs. Additionally, depending on what type of user you are, and how you store data will also influence your decision when comparing the two disks.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) don’t have any moving parts and instead rely on flash memory. This means they have fast data transfers, faster than hard disk drives. An SSD storage device is built of a circuit board and may be as small as a stick of gum, making it portable and handy. That means that they have large storage capacity but they can fit in smaller devices, like laptops and tablets.

Additionally, they can withstand being bumped against or moved around without being damaged. Since they don’t have the potential for damaging data, magnetically intense objects won’t have a visible impact. To see our picks for the best SSDs in 2023, read this article.
A hard disk drive stores data on spinning disks, which makes it slower than a solid-state drive. HDD storage devices have stacks of rotating platters with a head that oscillates up and down in response to the platter’s rotation. Because the head can read and write data to the platters, the speed of the platter governs the read-write speed. A powerful magnetic field might destroy data since data is magnetically stored.

Because HDD data storage devices are heavier and more prone to damage if moved, they are more commonly installed in a desktop computer (PC) and used for long-term storage. Additionally, a standard HDD has storage space and storage capacity that beat a solid-state drive.
So, for example, if you are using your own computer, let’s say a laptop, and you need your operating system to load quickly, and need multiple tabs open and the possibility to switch between tabs effectively and swiftly, you’ll need SSD. The read/write speed of these hard drives and the sequential reads has the advantage over HDDs.
However, if you are working on a company PC, with extremely large files that you need to store long-term, SSD speeds will not be valuable. The higher speed of the SATA interface SSD uses will have no power over the longevity and trustworthiness of an HDD. To read a comprehensive guide to which one you need in 2023, click here.
Factors that Affect SSD Speed vs HDD Speed
The speed of an SSD drive or HDD drive can be affected by a variety of factors, including the type of drive, the type of connection, and the size of the files. To test your own hard drive speeds, read this guide.
SSD speed is usually faster than that of an HDD. This is because SSDs use flash memory, which is significantly faster than the spinning disks used in HDDs.
The type of connection between the drive and the computer can also affect speed. SATA III is the fastest interface currently available, with speeds up to 6 Gbps. However, even a slower SATA interface can provide significant speed improvements over USB 2.0 or 3.0.
The size of the files also influences the speed of the hard drive. SSDs are much faster than HDDs when copying and reading small files. For medium files, SSDs are still faster than HDDs when copying, but there is not as big of a difference when reading. For large files, SSDs are slightly slower than HDDs when copying, but they are much faster when reading.
Is SSD faster at reading data than HDD?
SSDs are constructed for both greater read-write speed and are frequently used in applications that require speed rather than long-term backups. An SSD reads and writes data at speeds between 200MB/s and 550MB/s, compared to a normal HDD’s average of 80MB/s to 160MB/s. Faster speeds are available thanks to more contemporary technology, but the cost is substantially more than with traditional storage drives.
Is SSD faster at writing data than HDD?
As flash memory, an SSD can write data more quickly than an HDD. Keep in mind that an SSD loses quality over time if data is overwritten during read-erase-write operations. Maintaining lots of free space on the SSD is usually seen to be a good idea since overwritten data occurs more frequently when the SSD is full. Additionally, as HDDs can now store more data, they are favored for long-term storage applications that need fewer reads, such as storage reservoirs for backups and disaster recovery.
SSD Speeds vs HDD Speeds – Test SSD Speed
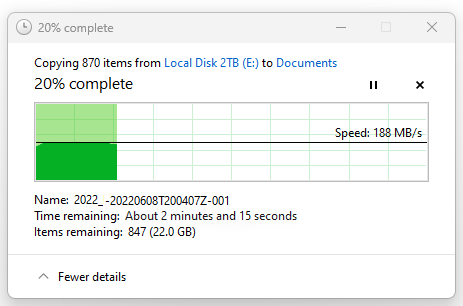
We conducted a series of speed tests on both SSD and HDD. You, too, can determine the read and write speeds for both HDD and SSD storage using benchmarking software to see which storage device is quicker. Drive manufacturers like Crucial, Samsung, Intel, and SanDisk (Western Digital) offer benchmarking tools so you can check drive speeds.
Here are our results:
Test 1: File Transfer Speed
For our first test, we transferred a 4GB file from one device to another. Here are the average transfer speeds:
- SSD: 400 MB/s
- HDD: 70 MB/s
As you can see, SSD is much faster than HDD when it comes to file transfer speed.
Test 2: Random Access Time
Next, we tested the random access time of both SSD and HDD. This measures how long it takes for the devices to access a particular file. Here are the average times:
- SSD: 0.15 ms
- HDD: 4.2 ms
Once again, SSD is much faster than HDD when it comes to random access time.
Test 3: Boot Time
Finally, we tested the boot time of both SSD and HDD. This measures how long it takes for the devices to boot up. Here are the average times:
- SSD: 8 seconds
- HDD: 30 seconds
As you can see, SSD drives are significantly faster than HDD drives when it comes to boot time.
Overall, our tests have shown that SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs in terms of file transfer speed, random access time, and boot time.
According to a study by Backblaze, a cloud storage company, SSDs can read and write data up to 10 times faster than HDDs.
NVMe drives vs SSD drives

For flash and next-generation solid-state drives (SSDs), NVMe (nonvolatile memory express) is a revolutionary storage access and transport protocol that offers the greatest bandwidth and quickest reaction times ever for all kinds of commercial applications.
It may be between 2 and 7 times quicker than SATA SSDs. NVMe can support up to 64,000 queues, each of which can process 64,000 instructions simultaneously.
Standard SSDs continue to use the outdated SATA interface, which has speed limitations.
A NVMe drive connects directly to the motherboard and CPUs through the quicker PCIe bus interface. Thus, it seems that NVMe hosting companies will provide speedier services than their traditional SSD rivals.
When used in a suitable device, NVMe SSDs offer considerable speed gains over SATA SSDs and can boost your PC’s overall performance. Instead of replacing your PC or laptop, you may revitalize it for a lot less money by upgrading it.
How To Improve A Slow Hard Drive?
Your hard disk might have a slower read and write time for a number of reasons. Those can include insufficient RAM, obsolete BIOS firmware, a disk that is contaminated with viruses, and a disk that has the TRIM command disabled. You could locate and fix the SSD writing performance issue with a third-party program.
However, if it is your RAM, it might be time to improve it on your computer (PC or a laptop), as SSD can be as fast as the RAM allows it. If it is a virus, you can easily scrub it and set up anti-virus apps that will protect your computer from unsafe connections.
In addition, you may download the most recent firmware or SSD drivers for your PC and check the SATA cable or connection.
Conclusion
After numerous examples, it is clear that SSDs are the faster option when compared to HDDs. While they do come at a higher price point, the improved performance and reliability of an SSD make up for its cost in the long run.
For users who want greater data speeds, go for an SSD; otherwise, HDDs offer good enough read/write speeds as well as larger storage capacities. In any case, we hope you have found this guide helpful in making your decision on which one is right for your requirements.